How Hospitals Handle Hazardous Waste Disposal Safely And Effectively
Hospitals produce much waste daily. It includes medical tools, leftover medicines, and blood-soaked bandages. Some of this waste is regular trash, but other types can be dangerous. These dangerous materials are called biohazard waste. Hospitals dispose of hazardous waste to protect people, animals, and the environment.
Biohazard waste can spread illnesses, cause injuries, and even pollute water and soil if not handled right. So, every hospital has a strict plan for biohazard waste disposal. In this blog, we’ll look at each step hospitals take to manage hazardous waste disposal from beginning to end.
1. Sorting And Separating Waste At The Source
The first step in hazardous waste disposal is to separate the waste types right when they’re created. Different types of biohazard waste need to be handled in different ways, so hospitals separate it carefully. For example:
– Infectious Waste:
This includes items that may have germs, like used bandages, gloves, and anything that touched patients’ bodily fluids.
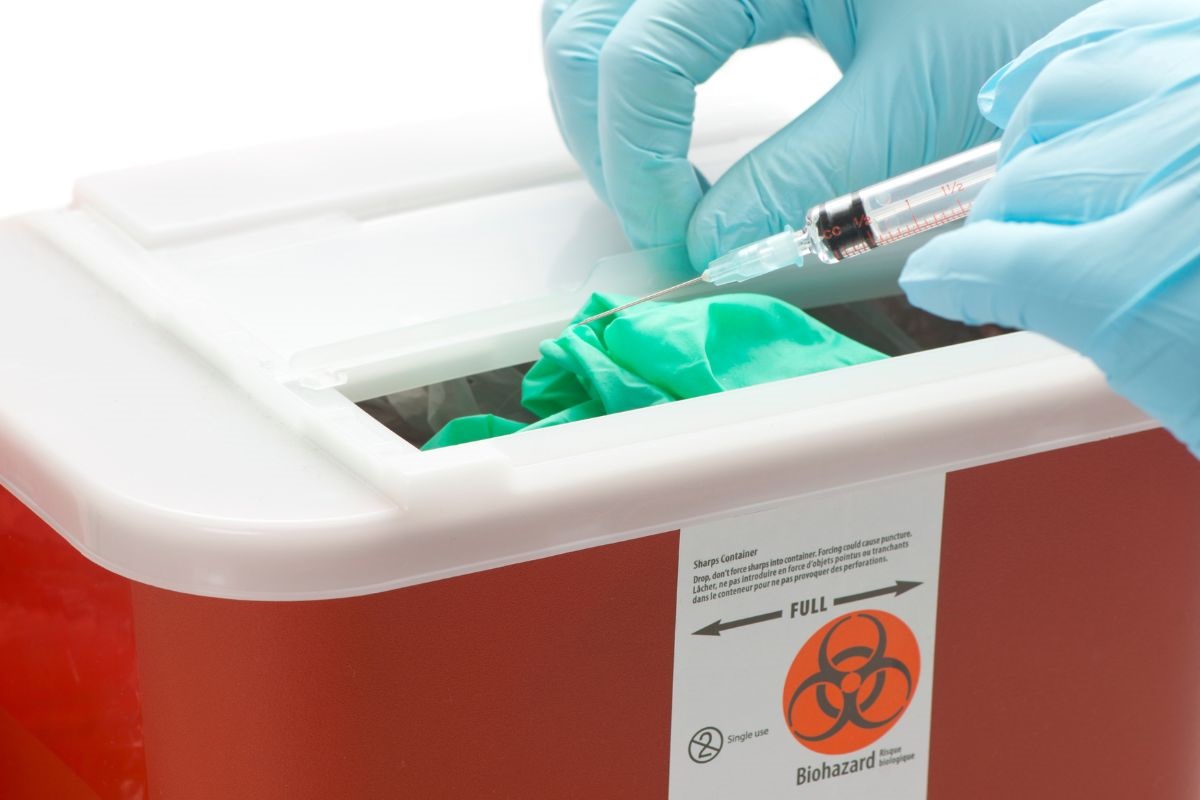
– Sharps Waste:
This includes needles, scalpels, and other items that could poke or cut someone. Because sharps can spread infection, hospitals use special, sturdy containers for them.
– Chemical Waste:
This waste includes old or expired medicines, cleaning chemicals, or lab chemicals. Chemical waste needs special handling to avoid causing harm.
Hospitals label each container clearly so that the staff knows what’s inside. Hazardous waste disposal starts by identifying each type and handling it in the safest way possible.
2. Proper Containment And Labeling
Once sorted, the next step is to put each type of waste into the right container. Hospitals use strong, sealed containers for hazardous waste disposal to prevent leaks or spills. Here’s a closer look at the containers used:
- Red biohazard bags: These bags are for things like bandages, gloves, and gowns that might have germs on them. They’re strong, and they clearly show that what’s inside could be dangerous.
- Sharps containers: These are sturdy, puncture-resistant boxes for things like needles and scalpels. When they’re full, they can be sealed completely to avoid accidental pokes or cuts.
- Chemical waste containers: Containers for old medicines or chemicals are labeled with special symbols. These symbols tell everyone that the contents are potentially toxic or harmful.
Labeling is also a big part of biohazard waste disposal. Containers often have labels with words or symbols, like a biohazard symbol or “dangerous.” This way, everyone handling the waste knows exactly what it is.
3. Moving Waste Safely Within The Hospital
When biohazard cleaning is done in one area, the waste has to be moved to a storage area in the hospital before it can be treated or sent away. Specially trained hospital staff carry or wheel the containers to make sure everything stays safe. They wear gloves, gowns, masks, and other protective gear to stay protected during the process.
To prevent any risk, hospital staff are trained to handle hazardous waste disposal with care. They follow rules about how to transport the waste without spilling or touching it. For example, they use carts or trolleys designed for moving biohazard waste. These carts keep the waste steady, reducing the chance of spills.
4. On-Site Waste Treatment Methods
After transport, some hospitals treat biohazard waste in their holding area. On-site treatment makes the waste safer by removing germs and harmful chemicals. Two of the most common on-site treatments are autoclaving and incineration.
Autoclaving
Autoclaving uses high-temperature steam to kill germs and make waste safe. This method is great for materials like bandages and certain medical tools. Here’s how it works:
- Waste is placed inside the autoclave.
- The machine heats up to a very high temperature and fills with steam.
- The steam kills any germs, bacteria, or viruses on the waste.
- Once it’s safe, the waste can be thrown away as regular trash.
Autoclaving is popular because it’s effective and doesn’t create harmful byproducts. It’s a key part of hazardous waste disposal in many hospitals.
Incineration
Some waste, like certain chemicals, needs to be completely destroyed. For this type of biohazard waste disposal, hospitals sometimes use incinerators. Incineration involves burning waste at very high temperatures until it turns into ash. This process destroys any germs, chemicals, or other dangerous materials.
Incineration is effective, but it must be controlled carefully to avoid pollution. Hospitals that use incineration have strict air-quality controls to keep the environment safe.
5. Off-Site Treatment By Certified Waste Disposal Companies
Sometimes, hospitals don’t have the equipment to treat all their waste on-site. In these cases, they rely on certified waste disposal companies that specialize in hazardous waste disposal. These companies pick up, transport, and treat the waste at their own facilities. Here’s how it works:
1. Collection:
- The disposal company picks up the waste directly from the hospital.
2. Transportation:
- The waste is transported in special trucks that are made to carry biohazard materials safely.
3. Treatment:
- At their facility, the company treats the waste by incinerating it, autoclaving it, or using other methods.
4. Disposal:
- Once the waste is treated and safe, it’s either disposed of in a landfill or recycled if possible.
These companies must follow strict rules and government standards to make sure all waste is treated safely. Hospitals work with certified companies to ensure safe biohazard waste disposal.
6. Final Steps In Safe Waste Disposal
Once waste has been treated and is no longer dangerous, it’s time for the final steps in hazardous waste disposal. Treated waste can be safely thrown away in landfills or disposed of as ash. Here’s what happens next:
- Landfills: Waste that’s been treated through autoclaving can be sent to a landfill. Since it’s no longer infectious, it won’t cause any harm.
- Ash Disposal: If the waste was incinerated, only ash remains. This ash can be buried in landfills as well, with little risk to the environment.
Hospitals have to follow all final disposal rules to make sure everything is handled safely from start to finish.
The Importance Of Training In Hazardous Waste Disposal
One reason hospitals are so good at managing biohazard waste disposal is that their staff receives a lot of training. Workers are taught exactly how to handle, transport, and treat biohazard waste. Training topics include:
- How to separate waste correctly
- How to use protective gear
- What to do if there’s a spill or accident
- How to follow all hazardous waste disposal rules
This training is repeated regularly to ensure all staff are prepared and knowledgeable. Biohazard cleaning is serious work, and hospitals make sure everyone knows how to do it safely.